Seagate Hard Drive Firmware Repair Tool Datasheet 2024
Seagate hard drive firmware repair tool-DFL-Seagate
Section 1: HDD Working Modes
Engineer can work in both ATA and COM terminal mode to diagnose and repair the HDD.
Section 2: Repair Modes
DFL Seagate firmware repair tool can do both hdd repair and hdd refurbishing, hdd repair is to fix firmware failures without affecting data but hdd refurbishing will remove bad sectors and destroy data.
Section 3: Number of HDD Supported by the DFL Seagate Hardware
Users can connect 3 drives to SRP portable Seagate hdd repair tool and 4 drives to PCIe Seagate hdd repair tool.
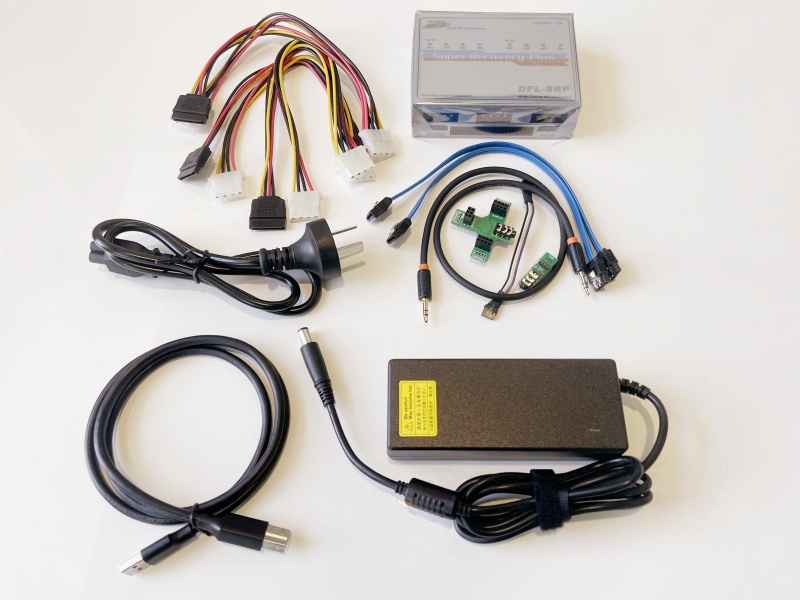

Section 4: Operating System to Install the software
Win 7, Win 8, Win 10, any of them is ok. DFL tools have unique driverless technology, no need to install device drivers.
Section 5: Biggest Advantages over Competitors
Easy to use and install on any pc, powerful with best technique support and data recovery resources.
Free data recovery training videos here: https://www.youtube.com/user/datarecoverytools
Section 6: What Kind of Seagate HDD Failures DFL Seagate can Fix
01: Seagate HDDs with many bad sectors;
02: Seagate HDDs with SA locked;
03: Seagate HDDs with ATA locked;
04: Wrongly detected Seagate hard drives;
05: 0 capacity detected Seagate hard drives;
06: Undetected/Busy Seagate hard drives;
07: Dead Seagate hard drives, to fix this kind of dead Seagate drives, users need to have ROM chip reader, donor PCB sources or physical head and platter swap tools to work with DFL Seagate firmware repair tool;
08: Seagate patient HDDs with LED status;
09: Seagate patient HDDs with weak heads;
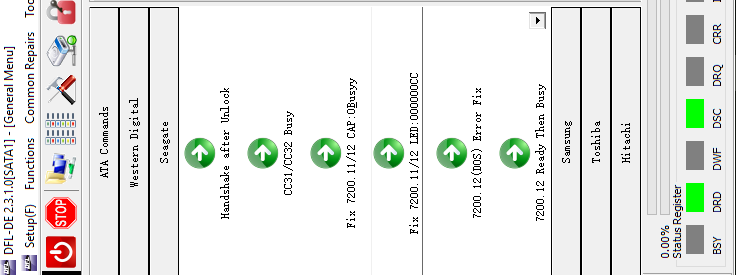
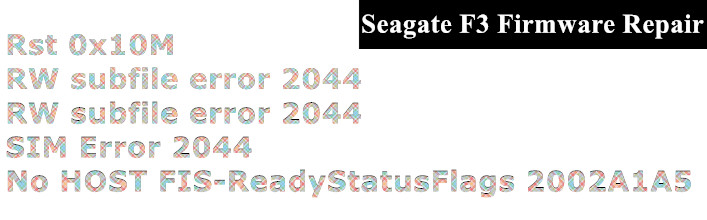
Section 7: Common Seagate HDD Firmware Failures-Quick Fix
01: Busy fix;
02: Capacity 0 fix;
03: Ready then Busy Fix;
04: DWF fix;
05: Sim 1002 fix;
06: Sim 1009 fix;
07: MCMT corruption fix;
08: Dos fix;
09: SMART fix;
10: LED fix;
11: Partial sector access fix;
12: Clear NG;
13: Remove password;
14: SMR HDD Format fix;
15: SSHD non-spin fix;
16: Clear media cache;
17: Load ATA/APP for old Seagate drive(Barracuda 7200.7-.10);
18: CELOG fix;
etc
Section 8: ROM Operations-Firmware on PCB
01: Read ROM by ATA or COM;
02: Write ROM by COM at any defined baud rates;
03: Head adaptive ROM;
04: CC49 ROM;
05: Edit head map in ROM;
06: Terminal/firmware unlock by generating and writing unlock rom;
07: Edit ROM;
08, Cut head in ROM;
09, Adjust Heads’ Working Temperature;
10, Disable Subsystem to fix LED issue;
11, Change ROM modules, write key original rom modules to donor ROM;
12: Nohost fix ROM generation;
Section 9: Service Area Operations-Firmware on Platters
01: Read/write firmware modules;
02: Read/write tracks;
03: Read/write/Edit SYS files;
04: Repair unknown firmware failures by tracks;
05: Repair unknown firmware failures by ABA;
06: Read/Write LOD;
07: Read/write SA;
08: Scan and record bad sector locations and add bad sectors to P-list;
09: Edit HDD ID (Model number/ LBA /SN number) and remove password;
10: Test SYS files;
Section 10: Service Area in RAM
01: Edit head map in RAM;
02: Load ATA in RAM;
03: Edit ID in RAM;
04: SAP Control flag;
05: Load translator to RAM;
06: Load ROM to RAM (for hot swap purpose);
Section 11: Defects Operations
01: Read/write/Edit G-list, P-list, NG list, Smart;
02: Delete non-SF defects in P-list, very helpful for fixing some sector access problems;
03: Delete specific defects on specific heads, this is usually used to cut heads for hdd refurbishing purpose;
04, Translator Clear and regeneration;
05: Translator Auto fix;
06, Format with Glist/Plist;
07: Offline bad sector repair;





Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!